One of the Cybercrime group has initiated attack against the job seekers and recruiters by attempting to steal log-in credentials for Monster.com and CareerBuilder.com accounts.
A new variant of the Gameover computer Trojan is being used by attackers for targeting users of popular employment websites with social engineering attacks, implemented to fetch additional private information about the victims, that could be used for bypassing multi-factor authentication mechanisms on other websites or services.
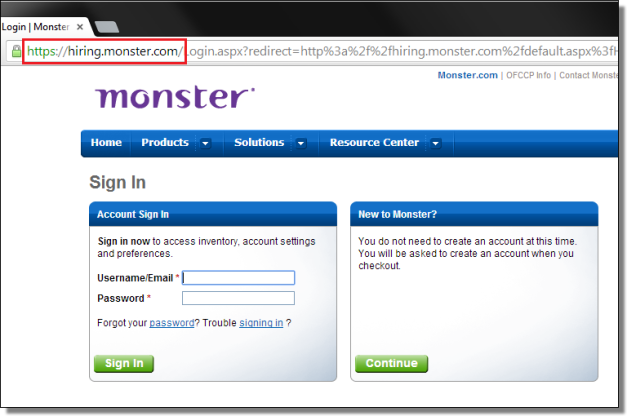
Once user tries to visit monster.com, they are served with the fake login page quite similar to the legitimate one(hiring.monster.com), but once the victim logs in, they are hijacked to the web page injected by the malicious code.
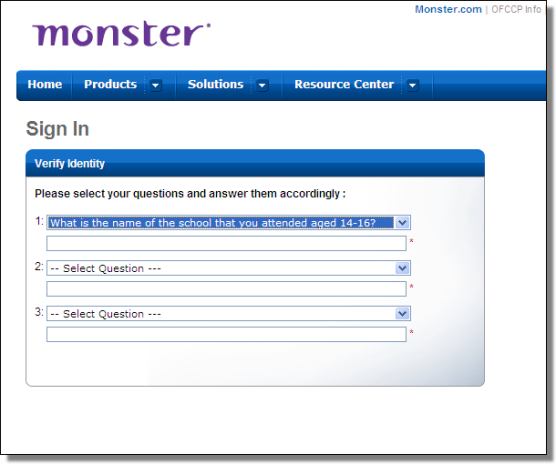
At this point the malware proposes to the victims 18 different security questions to choose from, the questions are requested via an injected form and a cookie called “qasent” is spawned by the process.
- In what City / Town does your nearest sibling live?
- In what City / Town was your first job?
- In what city did you meet your spouse/significant other?
- In what city or town did your mother and father meet?
- What are the last 5 digits / letters of your driver\’s license number?
- What is the first name of the boy or girl that you first dated?
- What is the first name of your first supervisor?
- What is the name of the first school you attended?
- What is the name of the school that you attended aged 14-16?
- What is the name of the street that you grew up on?
- What is the name of your favorite childhood friend?
- What is the street number of the first house you remember living in?
- What is your oldest sibling\’s birthday month and year? (e.g., January 1900)
- What is your youngest sibling\’s birthday?
- What month and day is your anniversary? (e.g January 2)
- What was the city where you were married?
- What was the first musical concert that you attended?
- What was your favorite activity in school?
Sean Sullivan, Security Advisor at F-Secure Labs, confirmed that it is hard to precisely count the number of victims because the Zeus Gameover is a P2P botnet.
“It’s a peer-to-peer botnet so it’s tricky to count,” ”There is some excellent analysis from Dell SecureWorks, which details about 24,000 Gameover bots, in July 2012. I haven’t seen any attempts to count the entireGameover botnet recently, but I’m sure it’s still in the multiple tens of thousands.” said Sullivan.
Security experts at F-Secure revealed the purpose of the attack is still a mystery, though it is likely designed to target the accounts of HR departments using Monster.
“HR recruiters with website accounts should be wary of any such irregularities. If the account is potentially tied to a bank account and a spending budget … it’s a target for banking trojans. It wouldn’t be a bad idea for sites such as Monster to introduce two factor authentication, beyond mere security questions.” said F-Secure expert Mikko Suominen.
Zeus Family:
Zeus Trojan is one of the most popular families of Banking Trojan, which was used in a targeted attack against a Salesforce.com customers last month and researchers found that the new variant of Zeus Trojan has capabilities that are used to fetch sensitive business data from that customer’s CRM instance.
Gameover is one of several Trojan programs that are based on the infamous Zeus banking malware, whose source code was leaked on the Internet in 2011. Like Zeus, Gameover can steal log-in credentials and other sensitive information by injecting rogue Web forms into legitimate websites when accessed from infected computers.